Facebook is scrambling to add safeguards against abuse of user data as it reels from backlash over the Cambridge Analytica scandal. Now TechCrunch has learned Facebook will launch a certification tool that demands that marketers guarantee email addresses used for ad targeting were rightfully attained. This new Custom Audiences certification tool was described by Facebook representatives to their marketing clients, according to two sources. Facebook will also prevent the sharing of Custom Audience data across Business accounts.
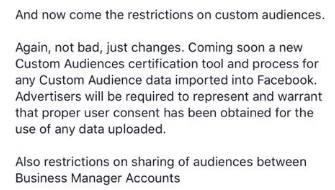 This snippet of a message sent by a Facebook rep to a client notes that “for any Custom Audiences data imported into Facebook, Advertisers will be required to represent and warrant that proper user content has been obtained.”
This snippet of a message sent by a Facebook rep to a client notes that “for any Custom Audiences data imported into Facebook, Advertisers will be required to represent and warrant that proper user content has been obtained.”
Once shown the message, Facebook spokesperson Elisabeth Diana told TechCrunch “I can confirm there is a permissions tool that we’re building.” It will require that advertisers and the agencies representing them pledge that “I certify that I have permission to use this data”, she said.
Diana noted that “We’ve always had terms in place to ensure that advertisers have consent for data they use but we’re going to make that much more prominent and educate advertisers on the way they can use the data.” The change isn’t in response to a specific incident, but Facebook does plan to re-review the way it works with third-party data measurement firms to ensure everything is responsibly used. This is a way to safeguard data” Diana concluded.The company declined to specify whether it’s ever blocked usage of a Custom Audience because it suspected the owner didn’t have user consent. ”
The social network is hoping to prevent further misuse of ill-gotten data after Dr. Aleksandr Kogan’s app that pulled data on 50 million Facebook users was passed to Cambridge Analytica in violation of Facebook policy. That sordid data is suspected to have been used by Cambridge Analytica to support the Trump and Brexit campaigns, which employed Custom Audiences to reach voters.
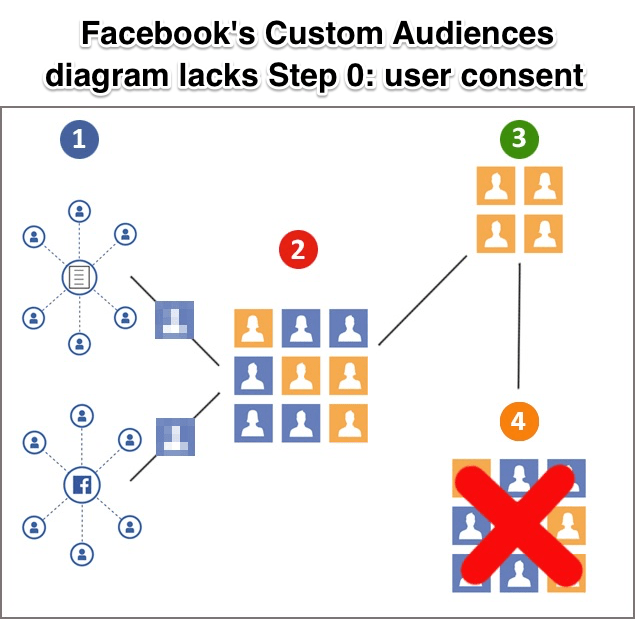
Facebook launched Custom Audiences back in 2012 to let businesses upload hashed lists of their customers email addresses or phone numbers, allowing advertisers to target specific people instead of broad demographics. Custom Audiences quickly became one of Facebook’s most powerful advertising options because businesses could easily reach existing customers to drive repeat sales. The Custom Audiences terms of service require that businesses have “provided appropriate notice to and secured any necessary consent from the data subjects” to attain and use these people’s contact info.
But just like Facebook’s policy told app developers like Kogan not to sell, share, or misuse data they collected from Facebook users, the company didn’t go further to enforce this rule. It essentially trusted that the fear of legal repercussions or suspension on Facebook would deter violations of both its app data privacy and Custom Audiences consent policies. With clear financial incentives to bend or break those rules and limited effort spent investigating to ensure compliance, Facebook left itself and its users open to exploitation.
 Last week Facebook banned the use of third-party data brokers like Experian and Acxiom for ad targeting, closing a marketing featured called Partner Categories. Facebook is believed to have been trying to prevent any ill-gotten data from being laundered through these data brokers and then directly imported to Facebook to target users. But that left open the option for businesses to compile illicit data sets or pull them from data brokers, then upload them to Facebook as Custom Audiences by themselves.
Last week Facebook banned the use of third-party data brokers like Experian and Acxiom for ad targeting, closing a marketing featured called Partner Categories. Facebook is believed to have been trying to prevent any ill-gotten data from being laundered through these data brokers and then directly imported to Facebook to target users. But that left open the option for businesses to compile illicit data sets or pull them from data brokers, then upload them to Facebook as Custom Audiences by themselves.
The Custom Audiences certification tool could close that loophole. It’s still being built, so Facebook wouldn’t say exactly how it will work. I asked if Facebook would scan uploaded user lists and try to match them against a database of suspicious data, but for now it sounds more like Facebook will merely require a written promise.
Meanwhile, barring the sharing of Custom Audiences between Business Accounts might prevent those with access to email lists from using them to promote companies unrelated to the one to which users gave their email address. Facebook declined to comment on how the new ban on Custom Audience sharing would work.
Now Facebook must find ways to thwart misuse of its targeting tools and audit anyone it suspects may have already violated its policies. Otherwise it may receive the ire of privacy-conscious users and critics, and strengthen the case for substantial regulation of its ads (though regulation could end up protecting Facebook from competitors who can’t afford compliance). Still the question remains why it took such a massive data privacy scandal for Facebook to take a tougher stance on requiring user consent for ad targeting. And given that written promises didn’t stop Kogan or Cambridge Analytica from misusing data, why would they stop advertisers bent on boosting profits?
For more on Facebook’s recent scandals, check out TechCrunch’s coverage:




 How to stop morale’s downward momentum will be one of Facebook’s greatest tests of leadership. This isn’t a bug to be squashed. It can’t just roll back a feature update. And an apology won’t suffice. It will have to expel or reeducate the leakers and disloyal without instilling a witchunt’s sense of dread. Compensation may have to jump upwards to keep talent aboard
How to stop morale’s downward momentum will be one of Facebook’s greatest tests of leadership. This isn’t a bug to be squashed. It can’t just roll back a feature update. And an apology won’t suffice. It will have to expel or reeducate the leakers and disloyal without instilling a witchunt’s sense of dread. Compensation may have to jump upwards to keep talent aboard 


 Like I said, when I visit a Google site, I expect that. But a browser is supposed to be a tool, not a private platform, and the idea that every tab I open is another data point and another opportunity for Google to foist its algorithms on me is rankling.
Like I said, when I visit a Google site, I expect that. But a browser is supposed to be a tool, not a private platform, and the idea that every tab I open is another data point and another opportunity for Google to foist its algorithms on me is rankling.